 https://blog.seneca.it/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/ac-power.jpg
https://blog.seneca.it/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/ac-power.jpg
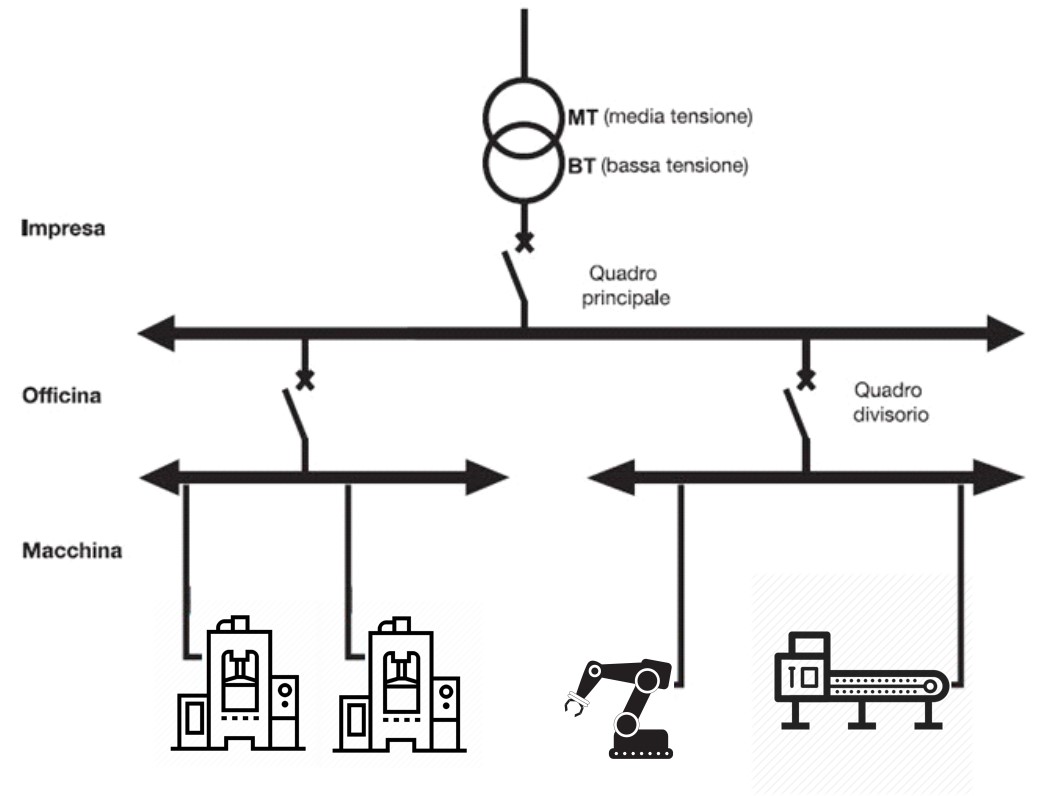
When designing an industrial electrical system, it is essential to consider the level of quality of the mains power supply available, and the appropriate supply voltages must be chosen according to this. Inside the automation, instrumentation and control panels are mounted both power equipment and electronic components (PLC, etc.) divided by screens and segregations to avoid possible problems of electrical failures and management of different power supply systems. This is why the selection, sizing and engineering of the switchboard must comply with standards and characteristics that, if well specified during the design phase, contribute to the proper functioning of the equipment as a whole and ensure the possibility of maintenance and evolution of the switchboard.
In the industrial sector the 24 V supply voltage has become a standard. Most manufacturers offer wide ranges of products and standardisation allows users to limit the risks of incompatibility between different products.
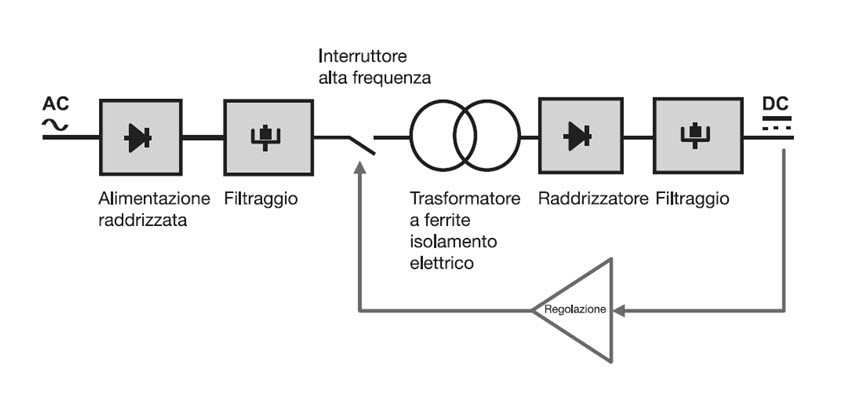
The benefits of Vac/Vdc switching power supply
SENECA provides a double range of 24 Vac/dc switching power supply on almost all its product range: I/O modules, controllers, RTUs, communication interfaces, network analyzers, energy meters, isolator-converters, stabilized power supplies, protections, digital indicators and batch controllers. The operating principle of a switching power supply is to switch a rectified voltage at high frequency. The availability of instruments with universal switching power supply Vac/dc offers the following advantages:
- Same module that can be supplied with both DC and AC power
- Stabilized output voltage value: constant, precise, linear
- Low dissipation (higher efficiency/energy efficiency, smaller switchboards)
- High performance without resorting to high peak powers
- Short circuit protection
- Rewiring or reconfiguration not required in case of AC/DC variation
- Continuity of service
- Absence of capacitive effect and noise in the cables
- Avoids the use of expensive and bulky transformers
- Lower power loss compared to transformers
- Lower cost compared to transformers (savings in the design and execution of the electrical panel)
- Management of a single sales code
The benefits of Vac power supply
Here are the main specific advantages of 24Vac power supply:
- Lower cost because a transformer is used instead of a stabilized power supply
- Higher reliability because the probability of failure of a transformer is lower than that of a stabilized power supply (higher MTBF)
- Greater safety because in the event of a short circuit in any part of the system, the arc generated by alternating voltage is less persistent than that of direct voltage, so there is less risk of fire in the equipment.
- Reduction of the risk of electrical hazard in severe or dangerous environments and less exposure of the instrumentation to risks arising from direct or indirect contacts, electric arcs and fire.
The benefits of Vdc power supply
The 24 Vdc power supply is preferable instead:
- In switchboards that for functional needs need DC voltage, such as switchboards in which the power supply is provided by batteries recharged by solar panels.
- In electrical panels installed in unmanned sites that need to remain powered even in the event of a mains power failure using backup batteries or uninterruptible power supplies
- In control panels with high concentration of controllers, I/O cards, solenoids, relays, solenoid valves and devices requiring 24Vdc power supply